Background and Motivation
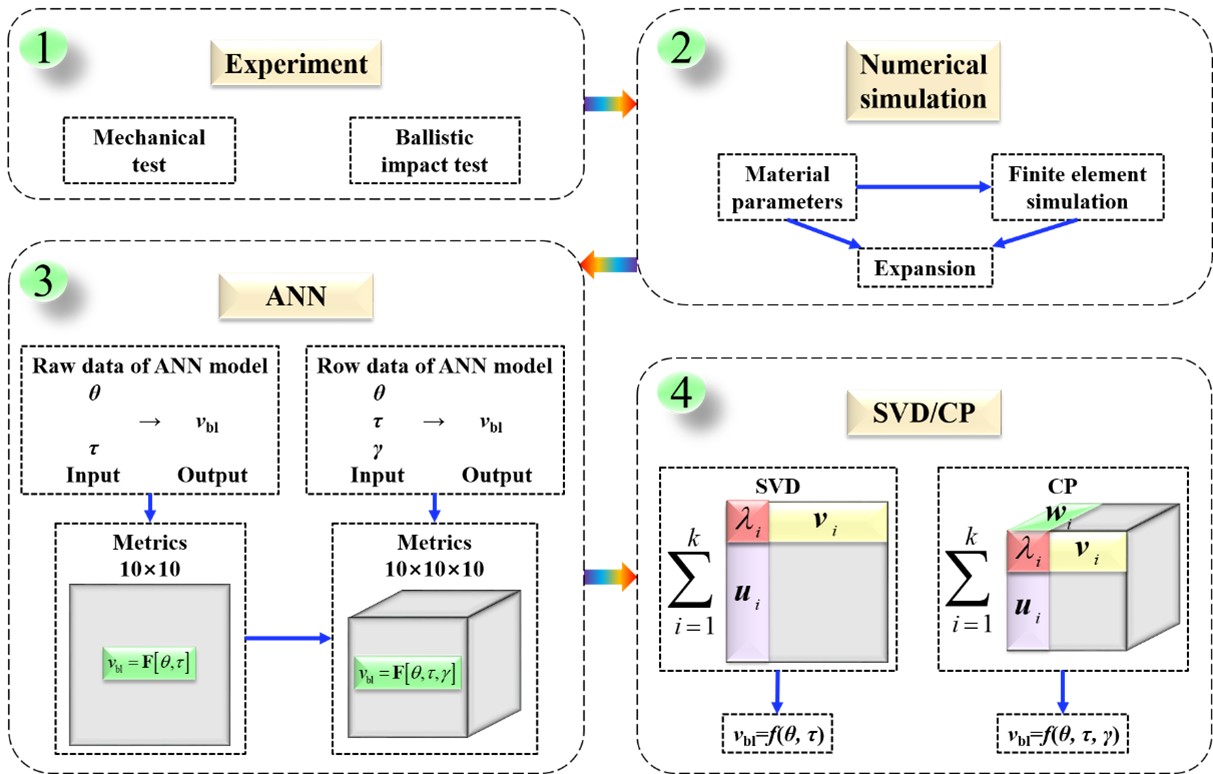
Ballistic resistance of finite-thickness materials is strongly influenced by multiple factors, including target thickness, impact angle, and projectile nose shape. However, conventional ballistic limit velocity (BLV) models are typically formulated for single, fixed impact scenarios and are unable to capture the coupled influence of these variables within a unified framework.
Experimental and numerical investigations across diverse impact conditions are costly and time-consuming, while the resulting data are often sparse and difficult to generalize. Consequently, establishing a reliable and decoupled ballistic resistance model based on limited multi-parameter data remains a significant challenge.
Motivated by these limitations, this work proposes a hybrid framework that integrates experiments, numerical simulations, and artificial neural networks to determine general ballistic resistance models. By exploiting data-driven decomposition techniques, the study aims to extract decoupled relationships between BLV and key impact parameters, enabling accurate and efficient prediction of ballistic resistance for finite-thickness materials.
Highlights
•
Artificial neural network is introduced and verified to be effective in the determination process of ballistic resistance model for finite thickness material.
•
The effect of the target thickness, impact angle and nose shape of projectile on the ballistic resistance is simultaneously considered in the modeling.
•
Decoupled relationships between ballistic limit velocity (typical representation of ballistic resistance behavior) and impact angle, target thickness, and nose shape of projectile are obtained respectively.
•
A general analytic ballistic resistance model considering impact angle, target thickness and nose shape of projectile is obtained with high accuracy.
•
A guided random sampling method, considering the data resolution, density ratio and distribution is proposed to collect small sample data for ANN training/validating usage.
Yunfei Deng, Xiaoyue Yang, Xianglin Huang*, Determination of ballistic resistance model of finite thickness material based on Artificial Neural Network, Thin-Walled Structures, Volume 203, 2024, 112161, ISSN 0263-8231, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2024.112161.